√100以上 sinus tachycardia vs svt in a child 308706-Sinus tachycardia vs svt in a child
0100 · The term supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) refers to any tachydysrhythmia arising from above the level of the Bundle of His, and encompasses regular atrial, irregular atrial, and regular atrioventricular tachycardias It is often used synonymously with AV nodal reentry tachycardia (AVNRT), a form of SVT In the absence of aberrant conduction (egSupraventricular tachycardia (SVT) can originate in either an ectopic atrial focus (atrial tachycardia) or the AV junction (junctional tachycardia) Differentiation from sinus tachycardia may be difficult, but is based on the following 1 With SVT the heart rate is inappropriately high for the horse's clinical condition, whereas with sinus · Atrial ectopic tachycardia (AET) is a rare arrhythmia;
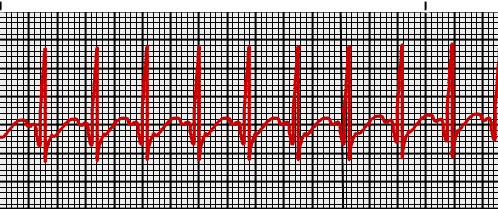
Supraventricular Tachycardia Vs Sinus Tachycardia Epomedicine
Sinus tachycardia vs svt in a child
Sinus tachycardia vs svt in a child- · Also, children with sinus tachycardia can be so fast, they appear to have PSVT The onset and offset can be excellent clues to the origin of the rhythm Sinus rhythms can be expected to speed up and slow down gradually, unlike PSVTs, which have sudden onset and offset The most important consideration is that sinus tachycardia usually has an APPARENT CAUSE exercise, · Neonatal Arrhythmias Elizabeth A Greene and George Van Hare DEFINITION Arrhythmias, alterations in the heartbeat rhythm, are a common problem in the newborn period Many are now diagnosed in utero We consider the tachycardias (rapid heart rhythms) first, then the bradycardias (slowed heart rhythms) TACHYCARDIAS The most commonly diagnosed fetal




Vagal Termination Of Ventricular Tachycardia In A Pediatric Patient American Academy Of Pediatrics
· What can be common between Sinus tachycardia and SVT?In both the cases, patients may be unstable In sinus tachycardia, due to untreated underlying cause like hypovolemic shock In SVT, due to primary electrical abnormality Both can commonly present with heart rate 150/min Narrow QRS complex (In an otherwise healthy adult, sinus tachycardia usually means a heart rate over 100 beats per minute Babies and children have faster resting heart rates than adults, so the criteria for sinus tachycardia is different For a baby, sinus tachycardia is usually means a heart rate over beats per minute
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is the most common rhythm disturbance in children 1 It is estimated to occur in as many as 1 in 250 otherwise healthy children Episodes are often recurrent and, although rarely life threatening, they may be life alteringStable Child Vagal manoeuvres and adenosine Vagal manoeuvres Valsalva if child old enough;2407 · Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Supraventricular tachycardias (SVT) are common in infancy and childhood, with an incidence between 1250 and11,000 In most cases it is due to a reentrant mechanism and usually occurs in otherwise normal children 3040% of children presenting with newonset SVT do so in the first few weeks after birth
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is the name given to the condition where the heart beats extremely fast but in a regular fashion for a period of minutes to hours Supraventricular means that the fast heart beat starts above the ventricles This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital describes SVT, what causes it and how it can · SVT tends to start and stop quickly, whereas sinus tachycardia has a gradual onset and resolution The patient should be asked about precipitating factors, suchGag or icepack/iced water for infants apply to face for a maximum of 30 seconds Do not use eyeball pressure Intravenous adenosine



1




Vagal Termination Of Ventricular Tachycardia In A Pediatric Patient American Academy Of Pediatrics
A normal heartbeat originates from the sinus node, the heart's pacemaker The electrical signal passes to the bottom of the heart through a special junction, called the AV node An abnormally fast heart rhythm (tachycardia) can arise from the upper or lower chambers of the heart, or be a 'circuitSupraventricular tachycardia is usually > 180 bpmSupraventricular tachycardia is usually > 180 bpm EKG Findings Important EKG findings in pediatric sinus tachycardia Heart rate will be < 2 bpm in an infant and < 180 bpm in children;




Differential Diagnosis Of Supraventricular Tachycardias Oxford Medicine
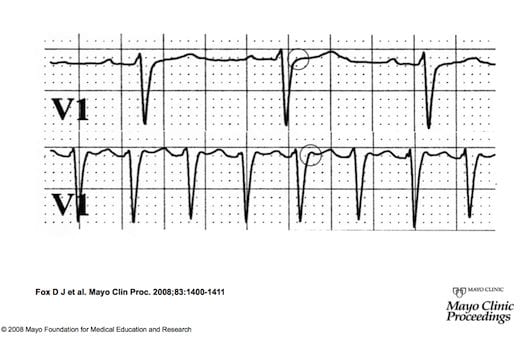



Supraventricular Tachycardia Svt Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis
SVT (supraventricular tachycardia) is an abnormally fast heart rate of over 100 heartbeats a minute Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a rapid heart rate (tachycardia, or a heart rate above 100 beats per minute) that is caused by electrical impulses thatSinus tachycardia (also colloquially known as sinus tach or sinus tachy) is an elevated sinus rhythm characterized by an increase in the rate of electrical impulses arising from the sinoatrial nodeIn adults, sinus tachycardia is defined as a heart rate greater than 100 beats/min (bpm) The normal resting heart rate is 60–100 bpm in an average male adult and 6090 bpm in an average · Up to 25% of children with congenital heart disease can present with SVT But also, children who have had SVT for more than 48 hours are often in heart failure when they present The prolonged tachycardia causes poor myocardial perfusion, so when they return to their normal rate they have a floppy myocardium that struggles to recover




Considerations In The Diagnosis And Emergency Management Of Pediatric Tachycardias 12 08 01 Ahc Media Continuing Medical Education Publishing




Tachyarrhythmias In Infants And Children
FIGURE1 medical app Discover medical cases from every specialty their views and advice DOWNLOAD NOW http//downloadfigure1com/greengloTachycardia vs Tachyarrhythmia Tachycardia Tachycardia is a term used to describe any heart rate that is rapid compared with the normal heart rate that should be present A "normal" rate is determined by the child's/infant's age "Normal" for the patient may also vary depending on the child's baselineSinus Tachycardia Sinus tachycardia is a normal increase in the heart rate In this condition, the heart's natural pacemaker, the sinoatrial (SA) node, sends out electrical signals faster than usual The heart rate is faster than normal, but the heart beats properly Causes of sinus tachycardia
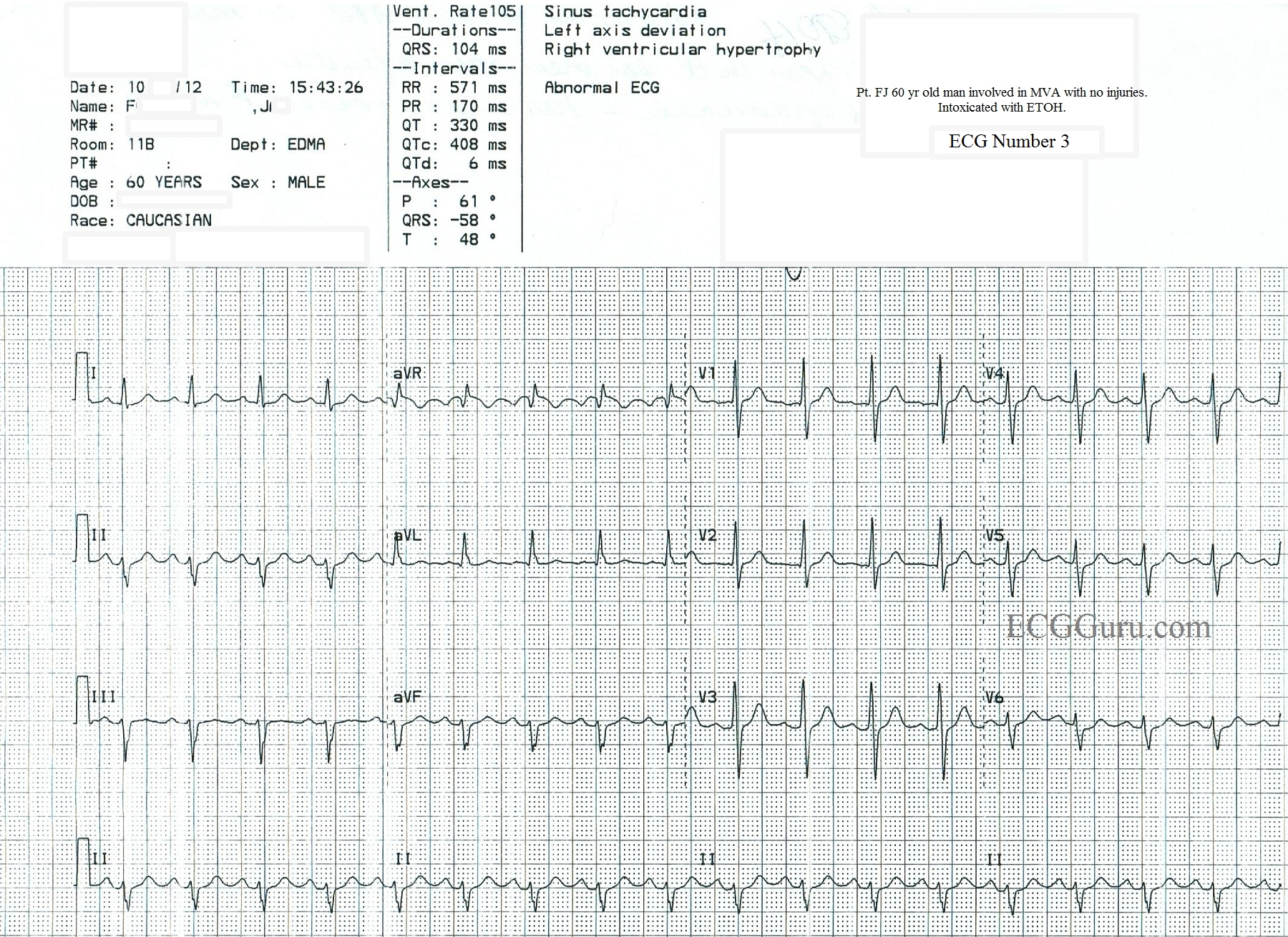



Sinus Tach Vs Svt In An Inebriated Patient Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Supraventricular Tachycardia Svt For Parents Children S Health System Alabama
Neonatal supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a common type of arrhythmia in newborn babies It causes episodes where the heart beats abnormally fast This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) explains the causes, symptoms and treatment of neonatal supraventricular tachycardia and where to get helpArrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms, which can preventSupraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is an arrhythmia or rapid heartbeat A normal heartbeat is caused by an electrical impulse traveling through the heart The electrical impulse originates in the sinus node (also called the sinoatrial node, or SA node), most often located in the top of the right atrium The electrical signals travel through theSinus tach is a normal heart rhythm, above 100 beats per minute SVT is a broad term used to describe many types of abnormal rhythms originating in the upper chambers of the heart (AVNRT, AFIB,WPW,EAT ect ect) Ide ask for clarification from your doctor in reguards to SVT causing the afib, since afib in itself technically is a type of SVT
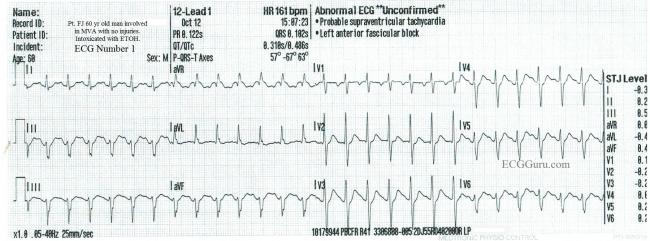



Sinus Tach Vs Svt In An Inebriated Patient Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Ecg Sinus Tachycardia Youtube
Tachycardia Treatment Treatment of tachycardia in children depends on the underlying cause Physiologic sinus tachycardia requires no treatment whatsoever Tachycardia due to an abnormal heart rhythm, for example SVT, usually requires either medication or a procedure to cure it · Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) SVT is common in adult and paediatric populations A more indepth overview of SVT, including in the adult patient, can be found here SVT is the most common dysrhythmia seen in the paediatric population, and comprises over 90% of paediatric dysrhythmias Of children presenting with SVT · Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a type of arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythm) in which the heart beats very quickly The abnormal heart rhythm starts in the atria, which are the top chambers of the heart Supraventricular tachycardia (soopruhvenTRIKyuhler takihKARdeeuh) often happens suddenly and can last for a few minutes or many



The Trouble With Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead




Diagnosis And Management Of Supraventricular Tachycardias Cmaj
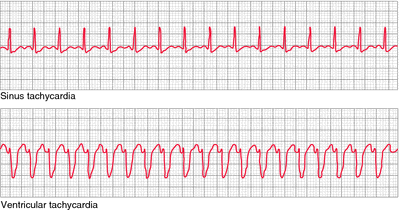
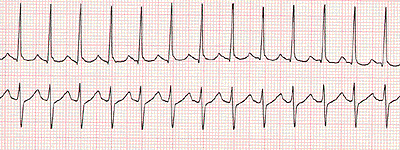
· Tachycardia or a fast heartbeat that's due to heart tissue abnormalities somewhere above the ventricles (lower chambers of the heart), is called supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) Causes of SVT in children and infants In most children, an electrical shortcircuiting causes SVT and is due to a small birth defectInfant Sinus tachycardia is usually < 2 bpm; · Sinus tachycardia has a rate of 100 to 150 beats per minute and SVT has a rate of 151 to 250 beats per minute With sinus tach, the P waves and T waves are separate With SVT, they are together




Recognising Supraventricular Tachycardia In Children An Arrhythmia Not To Miss Journal Of Paramedic Practice



The Trouble With Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a common arrhythmia in neonates SVT may initially be asymptomatic, but when prolonged it may result in congestive cardiac failure and shock after a variable period Other issues to note about SVT SVTs are defined as those requiring tissue above the bifurcation of the bundle of His for their continuanceSinus tachycardia is a regular heart beat more than 100 (per minute) The electrical impulse begins normally in the sinoatrial node and takes a normal pathway but the rate of these impulses is increased It is a normal response to exercise and occSupraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) and Atrial Tachycardia (AT) Fast heart rhythms (arrhythmias) that involve the upper chambers of the heart are often referred to as SVTs (supraventricular tachycardias) and can often be treated with an SVT ablation These arrhythmias cause the heart to suddenly beat very quickly due to an electrical 'short




Supraventricular Tachycardia Wikipedia



Sinus Tachycardia Definition Of Sinus Tachycardia By Medical Dictionary
Child Sinus tachycardia is usually < 180 bpm;Children can appear pale and can breathe faster and you may notice the veins in their neck twitching Children who can talk might say they have a funny or sore feeling in their chest or tummy SVT can last for seconds or hours and in some cases the feeling of weakness and tiredness can last after SVT has stoppedAn unsynchronised shock is necessary for ventricular fibrillation or polymorphic ventricular tachycardia;




Arrhythmias




Sinus Tachycardia Vs Svt On Ekg Medicine And Pharmacy Center Facebook
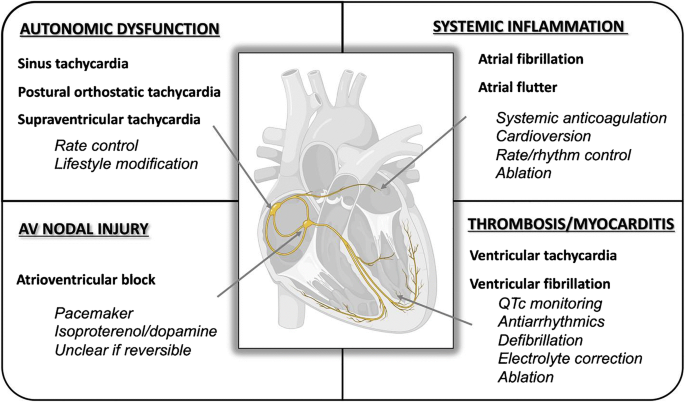
· Sinus tachycardia is when the sinus node in the heart sends electrical impulses faster than the normal rate, resulting in an increased heart rate Learn more in this article · Beyond SVT, only a few arrhythmias in association with DKA have been reported These include atrial fibrillation and sinus tachycardia that progressed to ventricular fibrillation Interestingly, quite a few similarities such as age, sex, and blood pH can be noted between these two cases and our patient · Infant Sinus tachycardia is usually < 2 bpm;




Supraventricular Tachycardia In Infancy And Childhood Pediatric Annals



Management Of Arrhythmias Associated With Covid 19 Springerlink
(SVT) SVT is used as a collective term Originates above the bundle of His Reentrant circuits generally have an abrupt onset and termination ie are paroxysmal (Hanash, 10) Sinus tachycardia Sinus node is faster than agerelated normal values due to enhanced automaticity Usually due to fever, pain, anxiety, anemia, medicationsSinus tachycardia can also be caused by increased thyroid activity or conditions such as anemia (low blood count), although rare In these instances, the tachycardia usually goes away once the underlying condition has been treated Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) The most common tachycardia in children is supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)However, it is the most common form of incessant supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) in children Atrial ectopic tachycardia is believed to be secondary to increased automaticity of a nonsinus atrial focus or foci




Svt In Infants A Crash Course




Supraventricular Tachycardia Ecg Causes Symptoms Treatment
FREE FREE FREE !!!Five children had some adverse effects However, none in the successful group of 13 patients required drug discontinuation because of such effects Onceaday oral atenolol as a monotherapy is effective and relatively safe for longterm management of SVT during childhoodWhat is supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)?




Supraventricular Tachycardia Wikipedia




Supraventricular Arrhythmias Clinical Framework And Common Scenarios For The Internist Mayo Clinic Proceedings
· Differentiation between SVT and VT To differentiate between supraventricular tachycardias and ventricular tachycardias a 12 lead ECG is the cornerstone of the diagnostic process At first, the physician has to make a differentiation between a narrow or wide complex tachycardia Definitions Narrow complex tachycardia QRS duration < 1 msSupraventricular tachycardia is usually > 2 bpm;As such, sinus tachycardia can be thought of as a sinusdriven rhythm (normalappearing P wave axis on the surface ECG) which is occurring at a rate of greater than 100 beats per minute However, the "normal" heart rate is, in part, the result of the complex interplay between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems




Pediatric Svt Vs Sinus Tachycardia Medictests




Atrial Tachycardia Diagnosis And Treatment The Cardiology Advisor
Supraventricular tachycardia is usually > 2 bpm Child Sinus tachycardia is usually < 180 bpm; · Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) The Most Common Tachycardia in Children SVT (Supraventricular Tachycardia) is the most common tachycardia in childrenAlso known as PSVT (Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia) and PAT (Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia), the condition isn't considered a serious life threat for young childrenIt is clearly true that V Tach is a more life threatening rhythm and that the treatment mode is very different from SVT Mechanism 1 Increased automaticity ( uncommon ) – If an irritable focus of the terminal Purkinje cells discharges at a rapid rate, > 150 bpm, this will produce a QRS complex as discussed previously (wide > 012 sec, bizarreshaped)




Pals Tachycardia Algorithm Learn Master Pals




Common Types Of Supraventricular Tachycardia Diagnosis And Management American Family Physician
This video demonstrates the treatment of a patient with supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) using adenosineInfants Diving reflex Place bag with ice slurry over face for




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog A Very Fast Narrow Complex Tachycardia In An Infant



Neonatal Arrhythmias Diagnosis Treatment And Clinical Outcome



Clinical Practice Guidelines Supraventricular Tachycardia Svt




15 Acc Aha Hrs Guideline For The Management Of Adult Patients With Supraventricular Tachycardia Circulation



Sinus Tachycardia Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia Ecg Echo



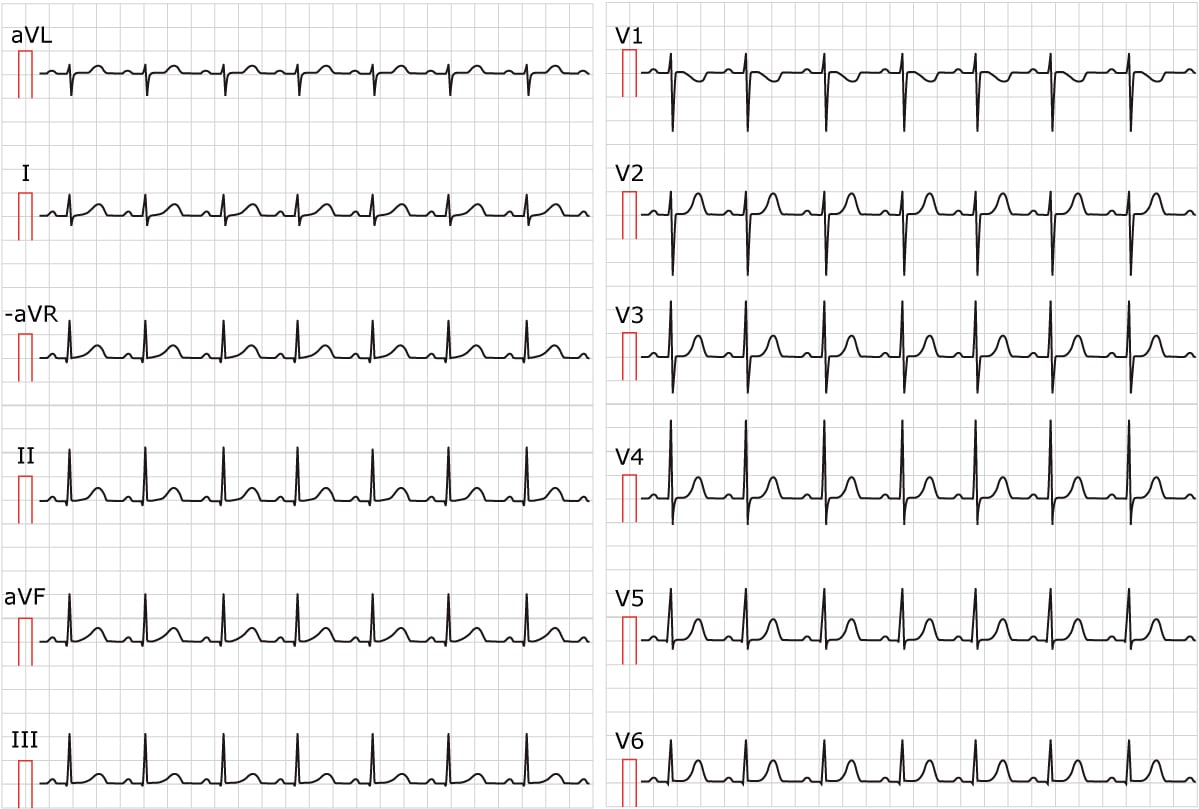
Supraventricular Tachycardia Svt Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Diagnosis And Management Of Common Types Of Supraventricular Tachycardia American Family Physician



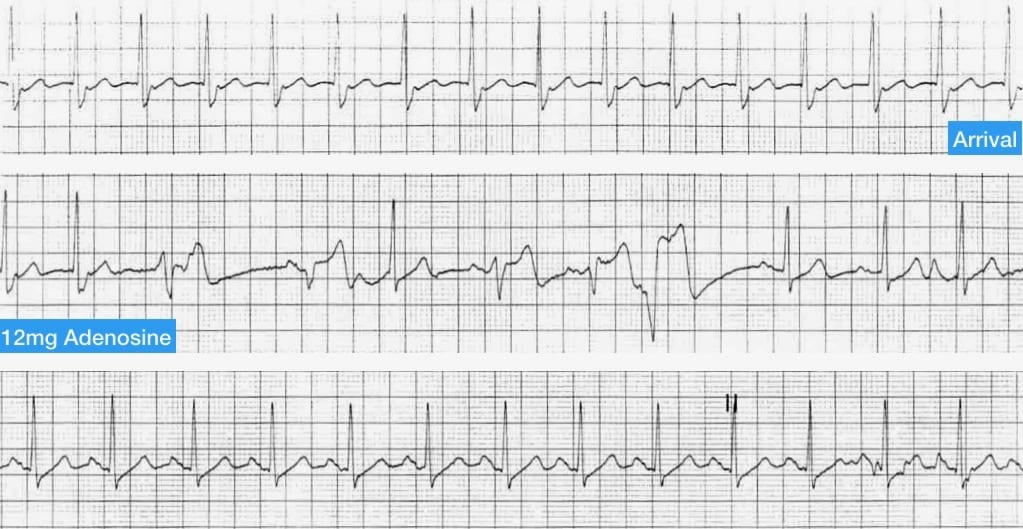
Pdf Supraventricular Tachycardia In Children




Assessing And Managing Pediatric Cardiac Rhythm Disturbances Jems




Premature Atrial Contraction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Common Types Of Supraventricular Tachycardia Diagnosis And Management American Family Physician



Pdf Supraventricular Tachycardia In Infancy And Childhood
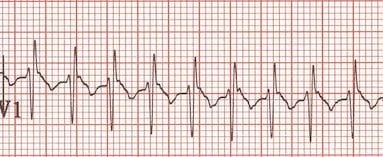



Common Paediatric Arrhythmias Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Supraventricular Tachycardia Svt Strategies For Diagnosis Risk Stratification And Management In The Emergency 02 02 11 Ahc Media Continuing Medical Education Publishing
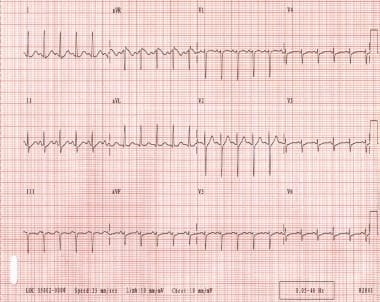



Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia Background Etiology Epidemiology



Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationtreatment Of Refractory Svt Pearls And Pitfalls Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education




Pediatric Svt Vs Sinus Tachycardia Medictests
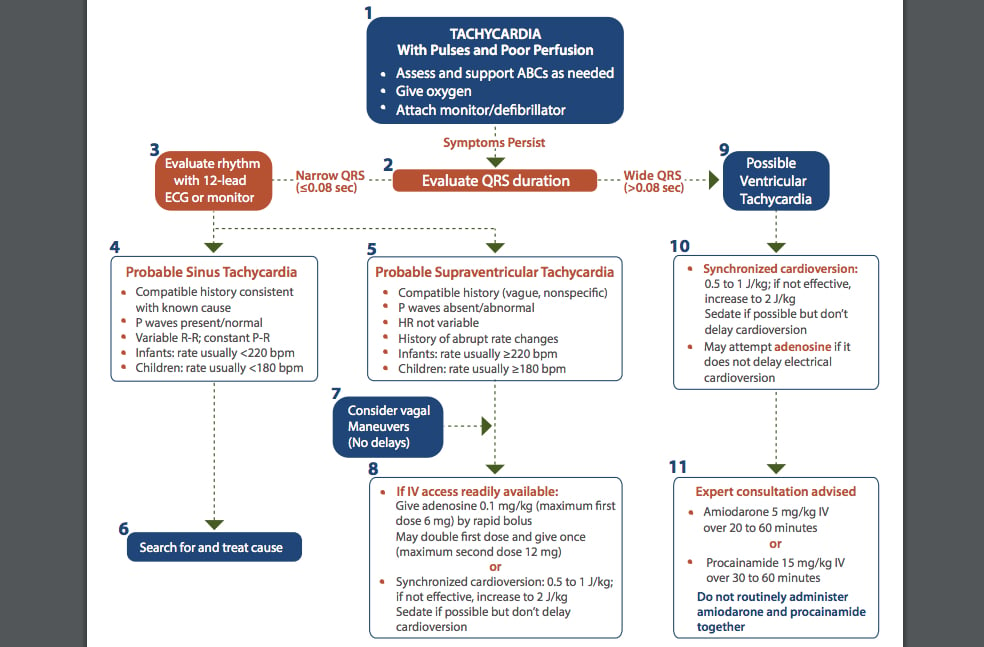



The Basics Of The Pediatric Tachycardia For Pediatric Advanced Life Support Daic
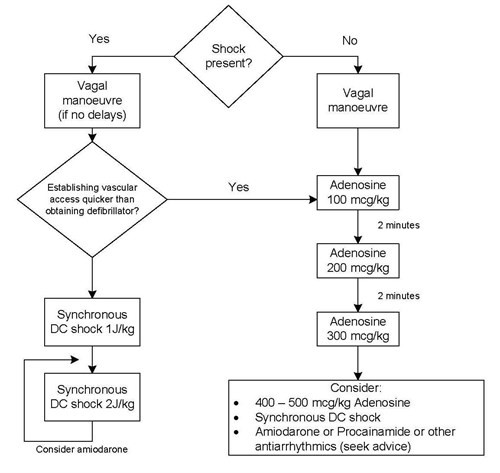



Tachyarrhythmia In Infants And Children




Svt Vs Sinus Tachycardia Part 2 Youtube




Common Types Of Supraventricular Tachycardia Diagnosis And Management American Family Physician
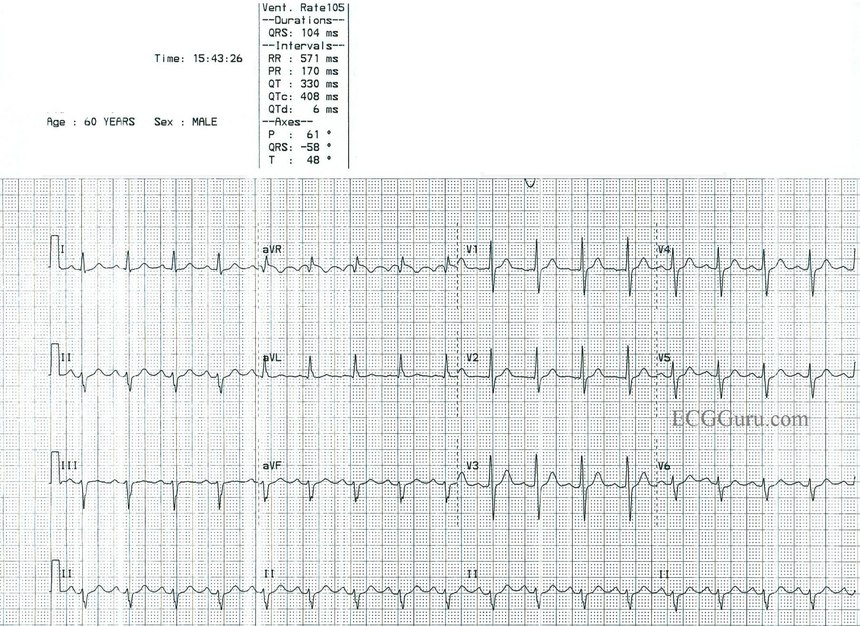



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference




Diagnosis And Management Of Common Types Of Supraventricular Tachycardia American Family Physician




Supraventricular Tachycardia Vs Sinus Tachycardia Epomedicine



Svt In Pediatrics



The Trouble With Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead



1




Sinus Tachycardia Vs Svt On Ekg Medicine And Pharmacy Center Facebook



1




Svt In Pediatrics
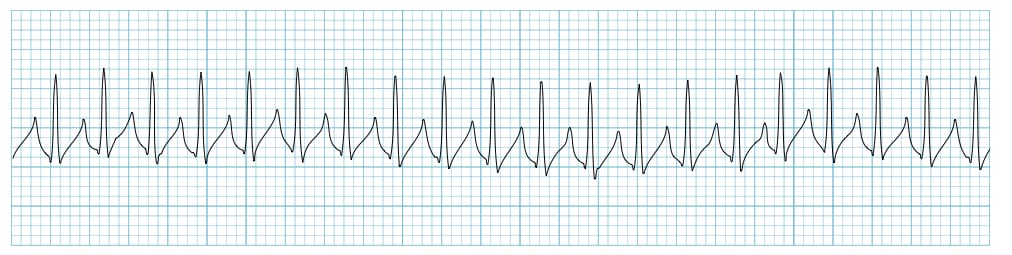



Supraventricular Tachycardia Svt Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis
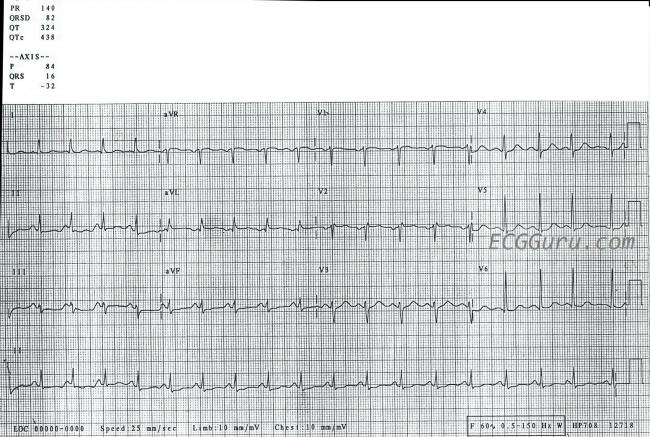



Sinus Tachycardia Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Pediatric Svt Em Sim Cases
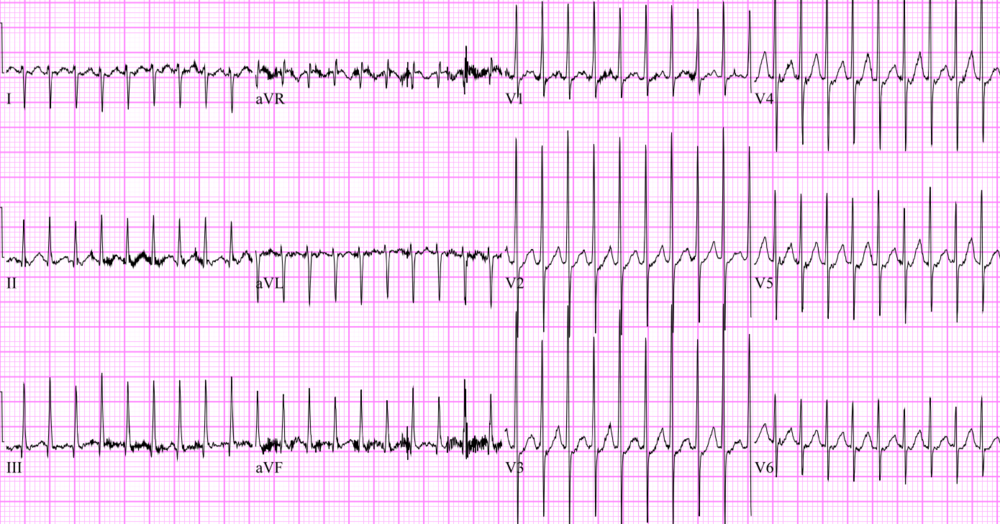



Annals Of B Pod Pediatric Svt Case And Expert Discussion Taming The Sru




Heart Rate 176 Min Sinus Tachycardia High Peaked P Wave Incomplete Download Scientific Diagram
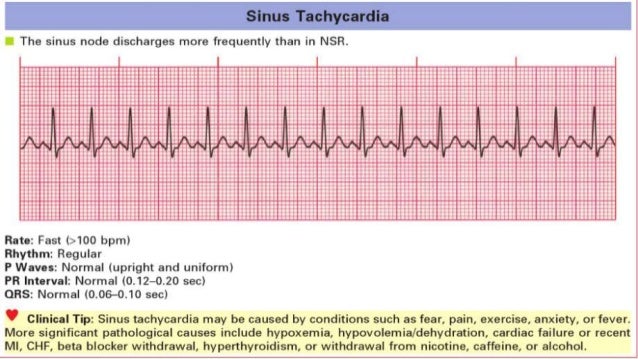



Cardiac Arrythmia In Children
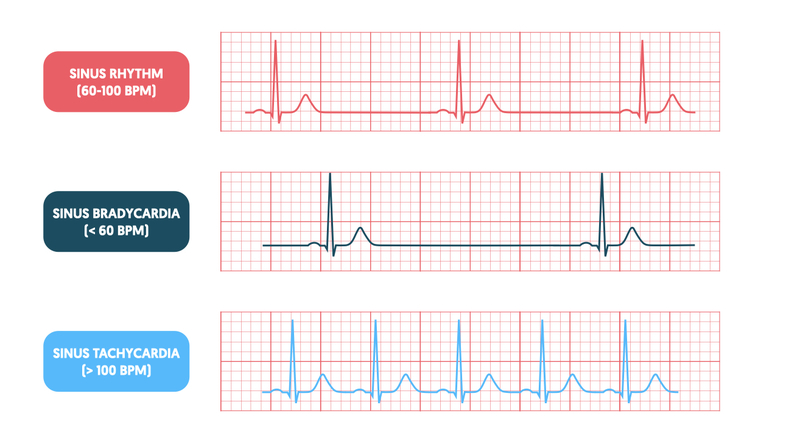



Pulsenotes Tachycardias




Pediatric Supraventricular Tachycardia And Sinus Tachycardia Medictests Com




Ventricular Tachycardia With No Structural Heart Disease Recognition And Treatment The Cardiology Advisor




Recognising Supraventricular Tachycardia In Children An Arrhythmia Not To Miss Journal Of Paramedic Practice




Neonatal Supraventricular Tachycardia Sciencedirect




Supraventricular Tachycardia Vs Sinus Tachycardia Epomedicine
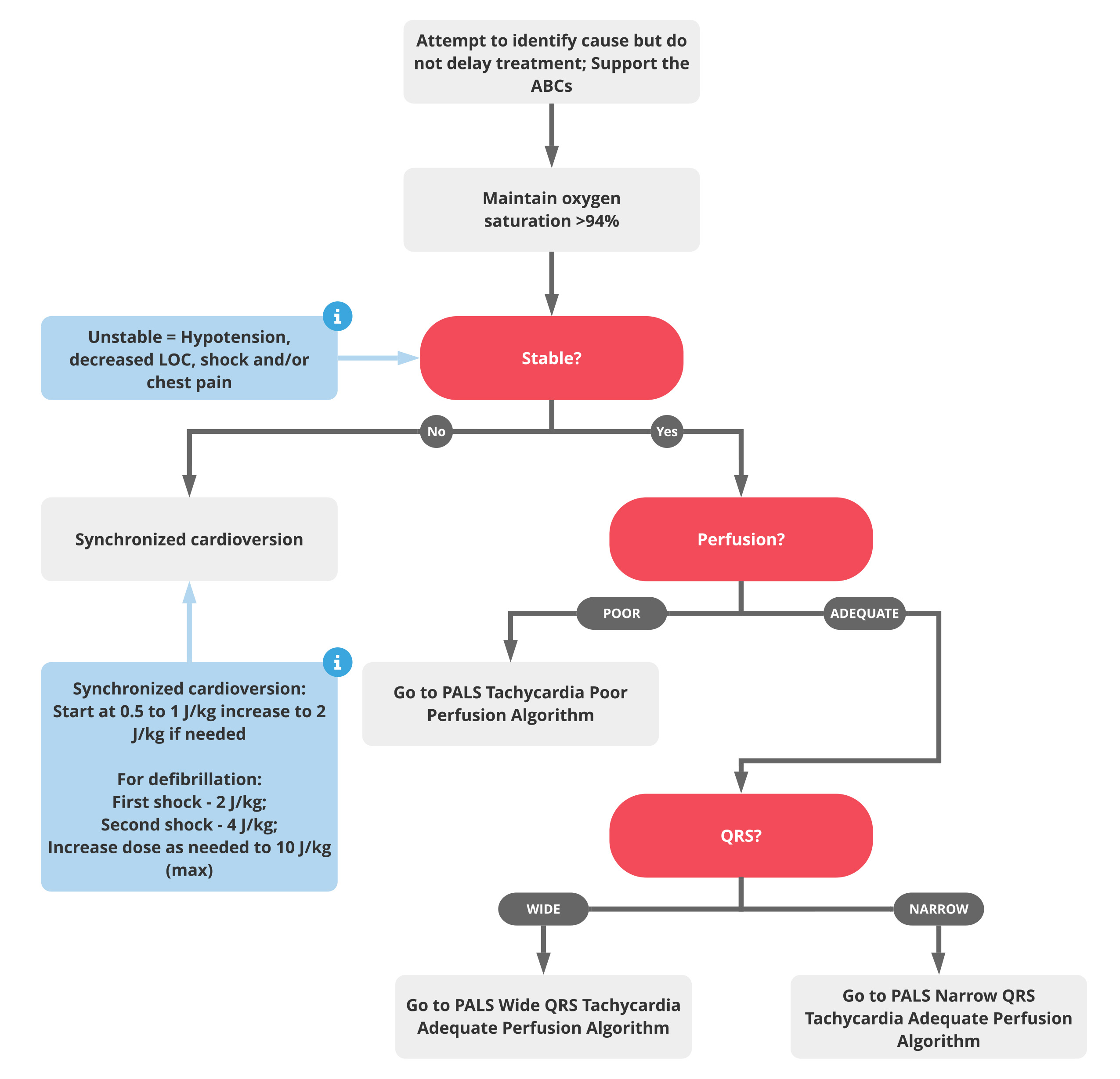



Pals Tachycardia Initial Management Algorithm Acls Medical Training




Managing Supraventricular Tachydysrhythmias In The Emergency Department
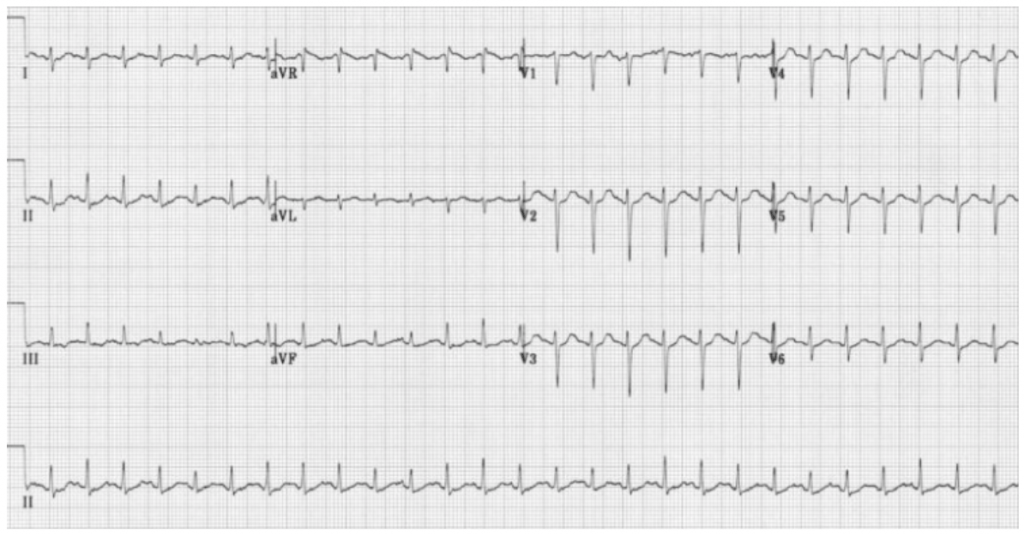



About Sinus Tachycardia Hope For Hearts Australia



1




Pals Tachycardia Algorithm Learn Master Pals
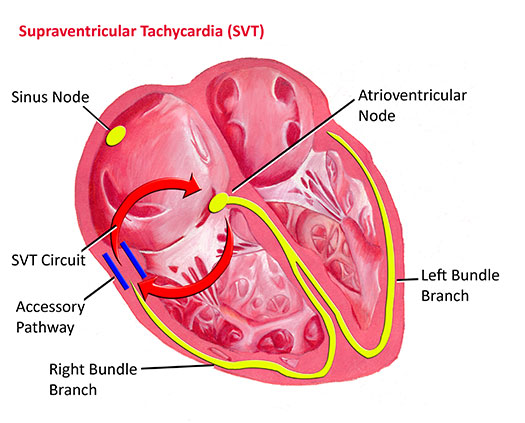



Supraventricular Tachycardia Pediatric Heart Specialists
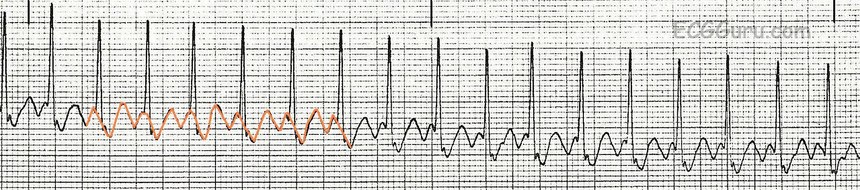



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference
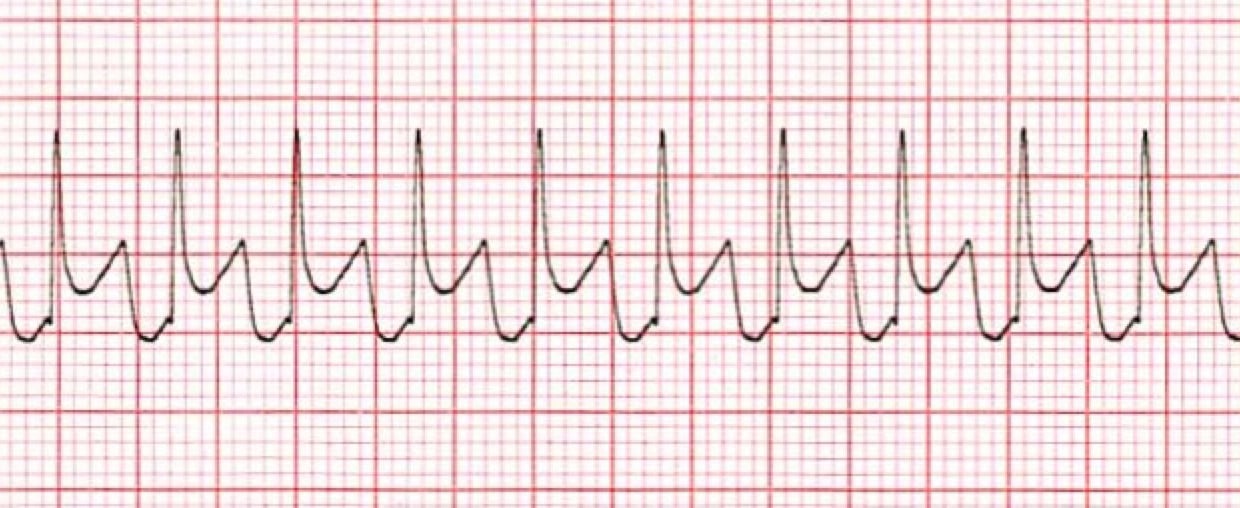



Supraventricular Tachycardia Training Cardiac Arrhythmias Video Propals



The Trouble With Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead




Sinus Tachycardia Wikipedia
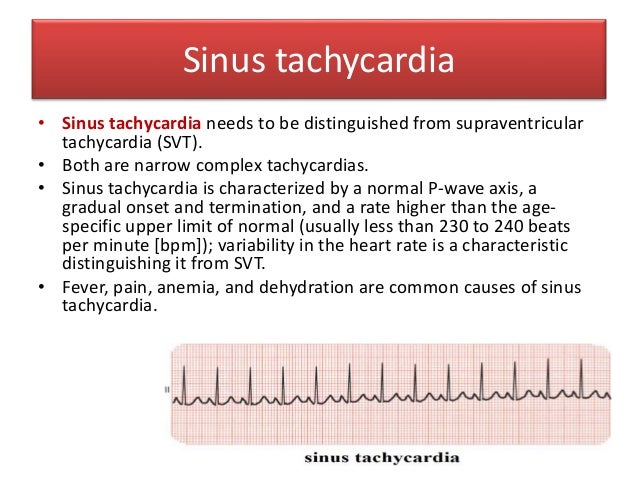



Palpitation In Children
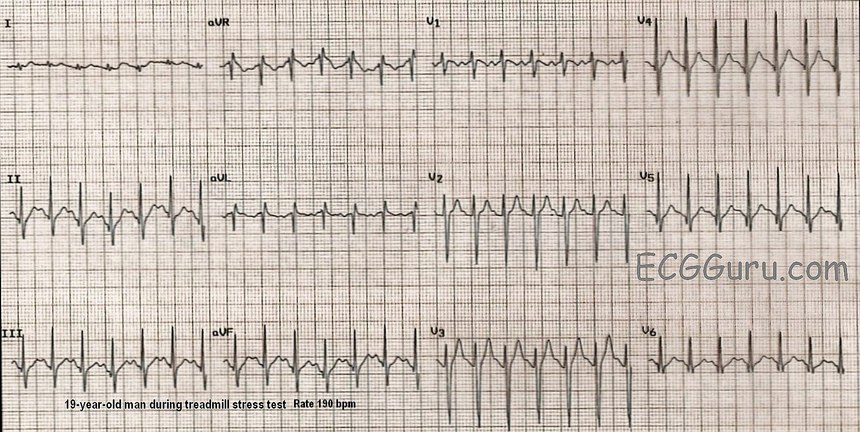



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference



The Trouble With Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead




Supraventricular Tachycardia Wikipedia
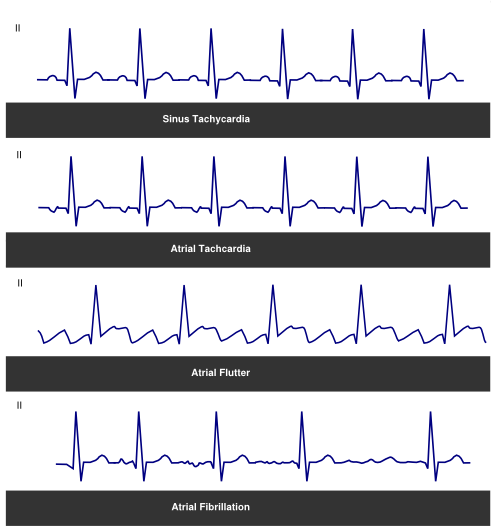



Tachycardia Textbook Of Cardiology




Supraventricular Tachycardia An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
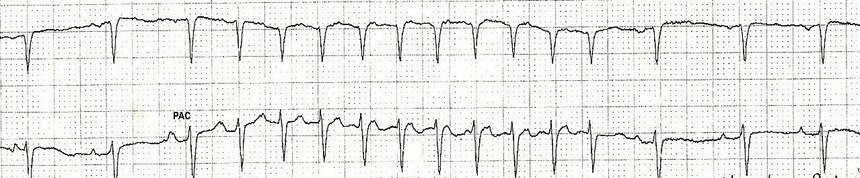



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference
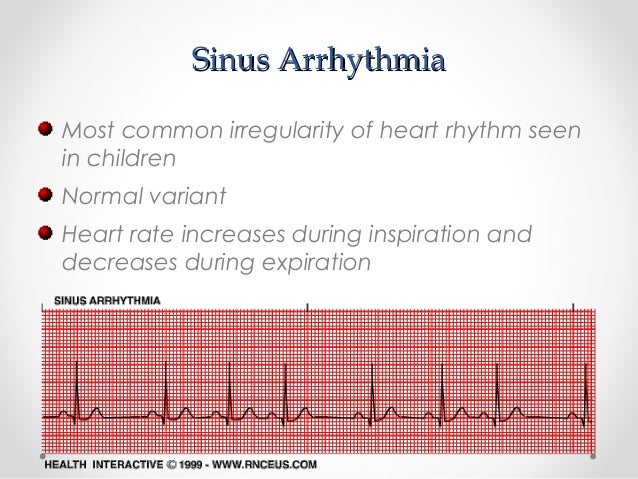



Svt In Pediatrics




Pin On Nursing




Arrhythmias




8 Svt Ideas Cardiac Nursing Svt Heart Nursing Students
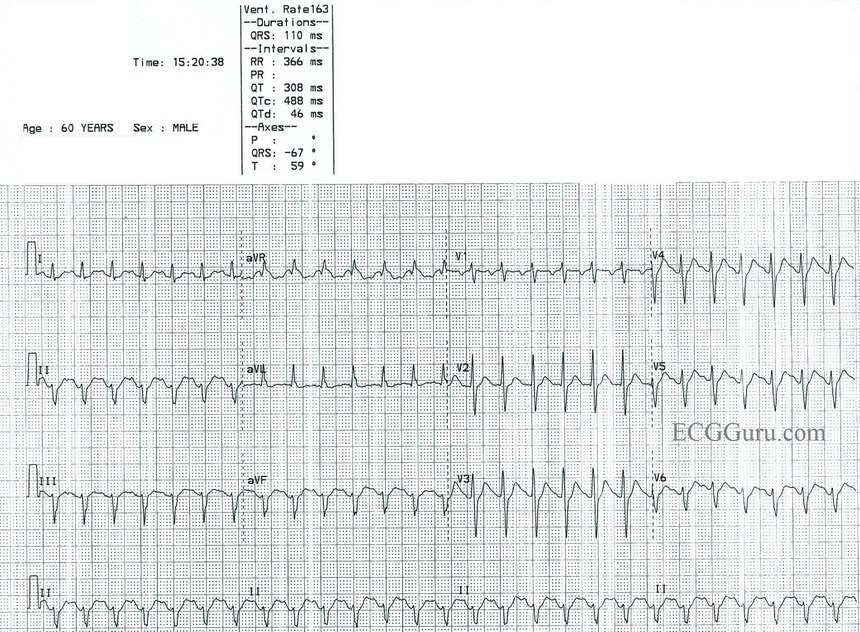



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference
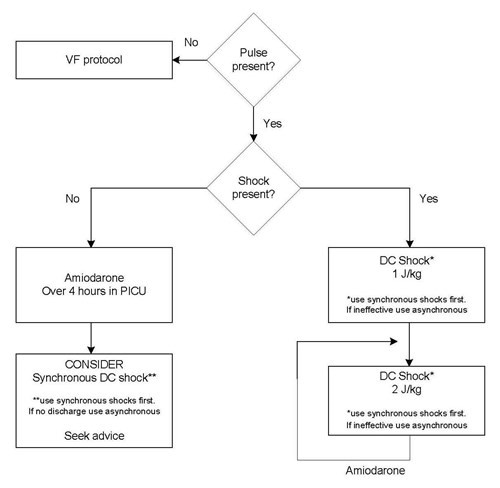



Tachyarrhythmia In Infants And Children
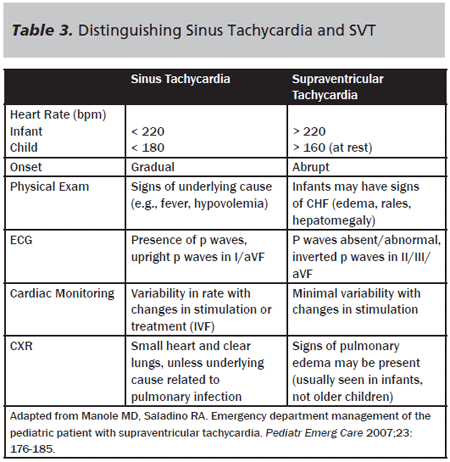



Supraventricular Tachycardia Vs Sinus Tachycardia Epomedicine
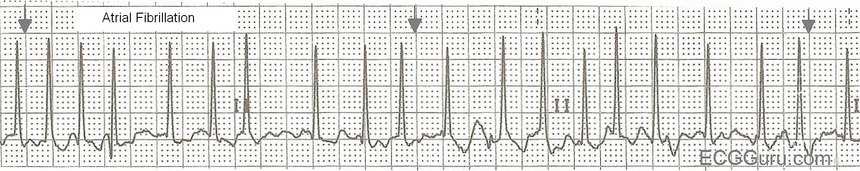



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference




Supraventricular Tachycardia Ppt Video Online Download




Pals Tachycardia Algorithm Learn Master Pals



Supraventricular Tachycardia Wikipedia
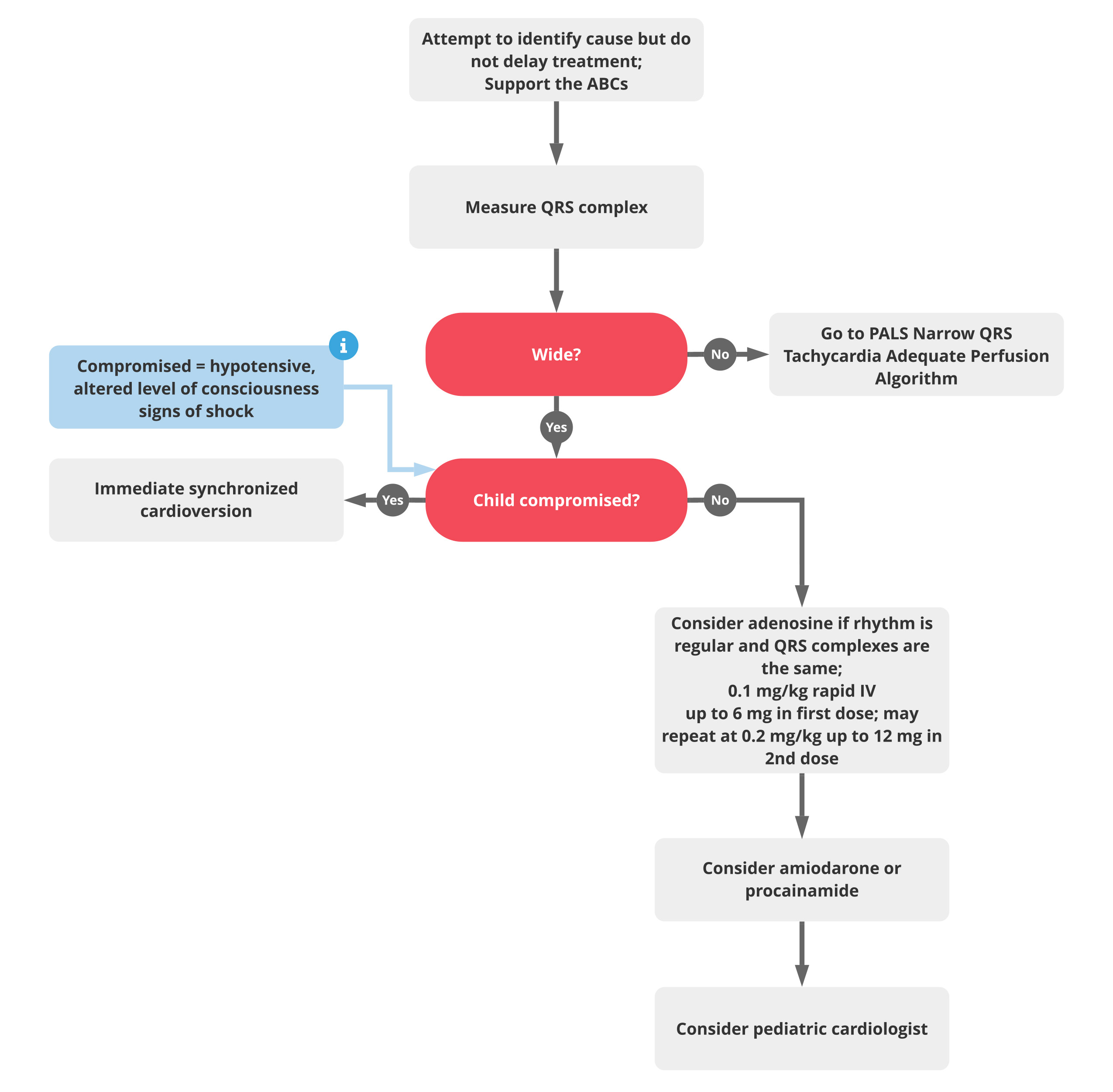



Pals Tachycardia Poor Perfusion Algorithm Acls Medical Training




Common Types Of Supraventricular Tachycardia Diagnosis And Management American Family Physician




Uhljxdqirfsium




Considerations In The Diagnosis And Emergency Management Of Pediatric Tachycardias 12 08 01 Ahc Media Continuing Medical Education Publishing




Diagnosis And Management Of Common Types Of Supraventricular Tachycardia American Family Physician
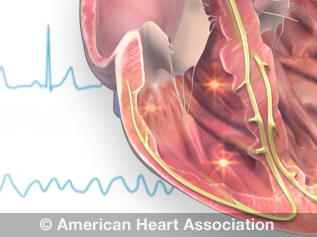



Types Of Arrhythmia In Children American Heart Association


コメント
コメントを投稿